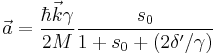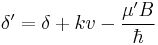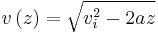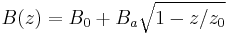Zeeman slower
A Zeeman slower is a scientific apparatus that is commonly used in experimental atomic, molecular, and optical physics to slow a beam of atoms or molecules from initial speeds on the order of 500 m/s-1000 m/s to final speeds on the order of 10 m/s (a few Kelvin). It consists of a cylinder, through which the beam travels, a pump laser that is shone on the beam in the direction opposite to the beam's motion, and a magnetic field (commonly produced by a solenoid-like coil) that points along the symmetry axis of the cylinder and varies spatially along the axis of the cylinder. The pump laser, which is required to be near-resonant to an atomic or molecular transition, Doppler slows a certain velocity class within the velocity distribution of the beam. The spatially varying Zeeman shift of the resonant frequency enables lower and lower velocity classes to be resonant with the laser, as the atomic or molecular beam propagates along the slower, hence slowing the beam.
Contents |
History
It was first developed by William D. Phillips (who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery in 1997 together with Steven Chu and Claude Cohen-Tannoudji "for development of methods to cool and trap atoms with laser light"[1]) and Harold J. Metcalf.[2] The achievement of these low temperatures lead the way for the experimental realisation of Bose-Einstein condensation, and a Zeeman slower can be part of such an apparatus.
Principle
According to the principles of Doppler cooling, an atom modelled as a two-level atom can be cooled using a laser. If it moves in a specific direction and encounters a counter-propagating laser beam resonant with its transition, it is very likely to absorb a photon. The absorption of this photon gives the atom a "kick" in the direction that is consistent with momentum conservation and brings the atom to its excited state. However, this state is unstable, and the atom will eventually (after a time on the order of the microsecond, for example in Rubidium 87 for the D2 transition 38 µs[3]) decay to its ground state. The photon will be reemitted (and the atom will again increase its speed), but its direction will be random. When averaging over a large number of these processes, one sees that the absorption process decreases the speed always in the same direction (as the absorbed photon comes from a monodirectional source), whereas the emission process does not lead to any change in the speed of the atom because the emission direction is random. Thus the atom is being effectively slowed down by the laser beam.
There is nevertheless a problem in this basic scheme because of the Doppler effect. The resonance of the atom is rather narrow (on the order of a few megaHertz), and after having decreased its momentum by a few recoil momenta, it is no longer in resonnance with the pump beam because in its frame, the frequency of the laser has shifted. The Zeeman slower[4] uses the fact that a magnetic field can change the resonance frequency of an atom using the Zeeman effect to tackle this problem.
The average acceleration (due to many photon absorption events over time) of an atom with mass,  , a cycling transition with frequency,
, a cycling transition with frequency, 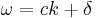 , and linewidth,
, and linewidth, 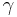 , that is in the presence of a laser beam that has wavenumber,
, that is in the presence of a laser beam that has wavenumber, 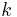 , and intensity
, and intensity 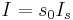 (where
(where 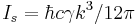 is the saturation intensity of the laser) is
is the saturation intensity of the laser) is
In the rest frame of the atoms with velocity, 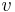 , in the atomic beam, the frequency of the laser beam is shifted by
, in the atomic beam, the frequency of the laser beam is shifted by 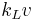 . In the presence of a magnetic field
. In the presence of a magnetic field 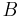 , the atomic transition is Zeeman shifted by an amount
, the atomic transition is Zeeman shifted by an amount 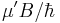 (where
(where 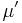 is the magnetic moment of the transition). Thus, the effective detuning of the laser from the zero-field resonant frequency of the atoms is
is the magnetic moment of the transition). Thus, the effective detuning of the laser from the zero-field resonant frequency of the atoms is
The atoms for which 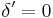 will experience the largest acceleration, namely
will experience the largest acceleration, namely
where 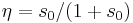 and
and 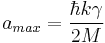 . We normally require that we have a magnetic field profile varies in the
. We normally require that we have a magnetic field profile varies in the 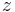 direction such that the atoms experience a constant acceleration
direction such that the atoms experience a constant acceleration 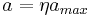 as they fly along the axis of the slower, so
as they fly along the axis of the slower, so
where 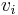 is the maximum velocity class that will be slowed; all the atoms in the velocity distribution that have velocities
is the maximum velocity class that will be slowed; all the atoms in the velocity distribution that have velocities  will be slowed, and those with velocities
will be slowed, and those with velocities  will not be slowed at all. The parameter
will not be slowed at all. The parameter 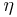 (which determines the required laser intensity) is normally chosen to be around .5. If a Zeeman slower were to be operated with
(which determines the required laser intensity) is normally chosen to be around .5. If a Zeeman slower were to be operated with 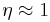 , then after absorbing a photon and moving to the excited state, the atom would then preferentially re-emit a photon in the direction of the laser beam (due to stimulated emission) which would counteract the slowing process.
, then after absorbing a photon and moving to the excited state, the atom would then preferentially re-emit a photon in the direction of the laser beam (due to stimulated emission) which would counteract the slowing process.
Realization
The required form of the spatially inhomogeneous magnetic field as we showed above has the form
This field can be realized a few different ways. The most popular design requires wrapping a current carrying wire with many layered windings where the field is strongest (around 20-50 windings) and few windings where the field is weak. An alternative design uses a single layer coil that varies rather in the pitch of the winding of such a coil.[5] Another proposed design uses an array of permanent magnets to create the field[6]..
Outgoing atoms
The Zeeman slower is usually used as a preliminary step to cool the atoms in order to trap them in a magneto-optical trap. Thus it aims at a final velocity of about 10 m/s (depending on the atom used), starting with a beam of atoms with a velocity of a few hundred meters per second. The final speed to be reached is a compromise between the technical difficulty of having a long Zeeman slower and the maximal speed allowed for an efficient loading into the trap.
A limitation of setup can is the transverse heating of the beam.[7] It is linked to the fluctuations of the speed along the three axis around its mean values, since the final speed was said to be an average over a large number of processes. These fluctuations are linked to the atom having a Brownian motion due to the random reemission of the absorbed photon. They may cause difficulties when loading the atoms in the next trap.
References
- ^ Nobel prize in physics press release, 1997
- ^ W. D. Phillips and H. Metcalf, Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 596 (1982)
- ^ Alkali D line Data, D. A. Steck
- ^ Bill Phillips' Nobel lecture
- ^ Bell et al. Review of Scientific Instruments. 81, 013105 (2010)
- ^ Zeeman slowers made simple with permanent magnets in a Halbach configuration, P. Cheiney, O. Carraz, D. Bartoszek-Bober, S. Faure, F. Vermersch, C. M. Fabre, G. L. Gattobigio, T. Lahaye, D. Guéry-Odelin, R. Mathevet
- ^ [www.quantumoptics.ethz.ch/papers/slower.pdf K. Günter Design and implementation of a Zeeman slower for Rb 87]